
Mangrove forests are unique and fascinating ecosystems found along the intertidal zones of coastlines, where freshwater meets saltwater. These forests are known for their rich biodiversity and are critical for maintaining the health of coastal ecosys Read more
Trending
Trees for Corporates
Top 10 Mangrove Forests in India: A Journey Through the Coastal Ecosys
Mangrove forests are unique and fascinating ecosystems found along the intertidal zones of coastlines, where freshwater meets saltwater. These forests are known for their rich biodiversity and are critical for maintaining the health of coastal ecosystems. India is home to some of the most beautiful and important mangrove forests in the world, which play a vital role in protecting the coastlines from erosion, storm surges, and tsunamis.

Here are the top 10 mangrove forests in India that every nature lover should explore:
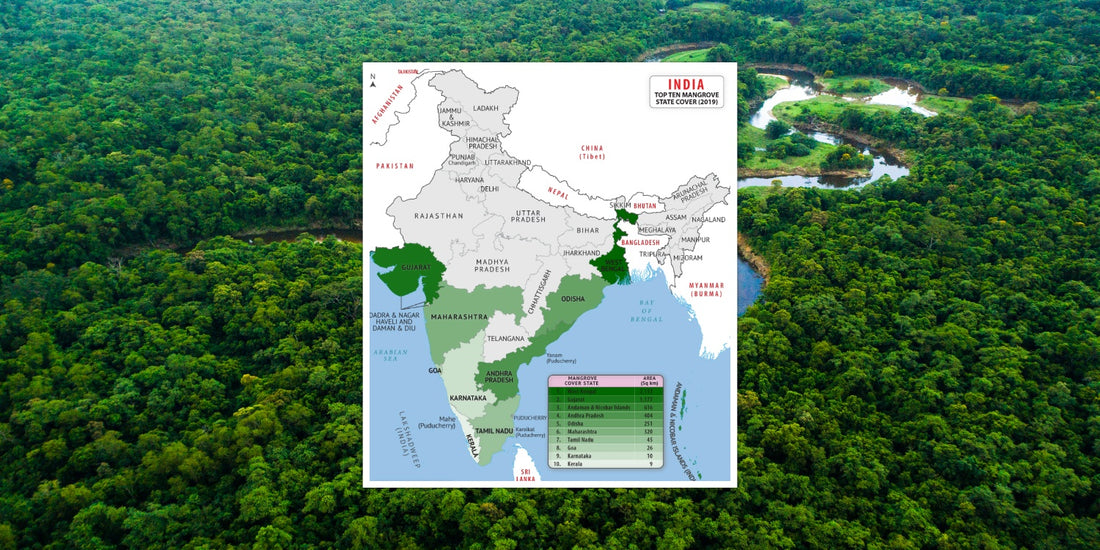
- Sundarbans Reserve Forest, West Bengal: The Sundarbans is the largest mangrove forest in India, and it is also the world's largest mangrove forest, covering an area of approximately 10,000 square kilometers. It is located in the delta of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers, and it is shared between India and Bangladesh. The Sundarbans is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is home to a variety of wildlife, including the Royal Bengal Tiger, estuarine crocodiles, and the Indian Gangetic Dolphin.
- Pichavaram mangrove forests, Tamil Nadu: Pichavaram is one of the largest mangrove forests in the world, covering an area of approximately 1100 hectares. It is located in the delta of the rivers Cauvery and Coleroon, and it is a popular destination for eco-tourism. The forest consists of various islands of different sizes, and it is home to a variety of bird species, including openbill storks, little egrets, cormorants, and pond herons.
- Bhitarkanika Mangroves, Odisha: The Bhitarkanika Mangroves are located in the delta of the rivers Brahmani and Baitarani, and they are famously called a genetic paradise of mangroves. This mangrove forest also houses the Bhitarkanika Wildlife Sanctuary and the Bhitarkanika National Park on its vast premises. The forest is home to a variety of wildlife, including saltwater crocodiles, Indian python, and the King Cobra.
- Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary, Andhra Pradesh: Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary is a protected area located in the Godavari delta, and it is the third-largest mangrove forest in India. The sanctuary is home to 24 different species of mangrove trees and over 120 different bird species. It is also a breeding ground for the endangered olive ridley turtles.
- Gulf of Kutch Mangroves, Gujarat: The mangroves of the Gulf of Kutch are considered one of the largest mangroves in India, and they are home to a variety of wildlife, including the endangered Bengal tiger. The forest is also a popular destination for birdwatching, as it is home to a variety of migratory birds, including flamingos, pelicans, and herons.
- Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary, Andhra Pradesh: The Krishna Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the delta of the Krishna River, and it is home to a variety of wildlife, including the Indian otter, estuarine crocodiles, and the Indian python. The sanctuary is also a popular destination for birdwatching, as it is home to a variety of migratory birds, including the Dalmatian pelican and the spot-billed pelican.
- Chorao Island Mangroves, Goa: Chorao Island is located in the Mandovi River, and it is home to a variety of mangrove species. The island is a popular destination for eco-tourism, as it offers a variety of activities, including birdwatching, boat rides, and nature walks.
- Baratang Island Mangroves, Andaman and Nicobar Islands: Baratang Island is located in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and it is home to a variety of mangrove species, including the grey mangrove. The island is a popular destination for eco-tourism, as it offers a variety of activities, including boat rides, nature walks, and birdwatching.
- Mumbai City and Suburban Areas: Mumbai city and its suburban areas are home to some of the most unique and diverse mangrove forests in Maharashtra. These forests are spread over an area of 65.22 square kilometers and are home to a variety of mangrove species, including Avicennia marina, Avicennia officinalis, and Sonneratia alba1. These forests are not only important for their biodiversity but also for their role in protecting the city from coastal erosion and storm surges1.
- Thane District: Thane district is home to some of the most beautiful and unique mangrove forests in Maharashtra. These forests are spread over an area of 118.15 square kilometers and are home to a variety of mangrove species, including Avicennia marina, Avicennia officinalis, and Bruguiera cylindrica1. These forests are not only important for their biodiversity but also for their role in protecting the district from coastal erosion and storm surges
- Mangroves are unique trees that can survive in both freshwater and saltwater environments.
- Mangroves have specialized root systems that allow them to filter salt from seawater.
- Mangroves provide a habitat for a variety of wildlife, including fish, crustaceans, and birds.
- Mangroves are critical for maintaining the health of coastal ecosystems, as they protect coastlines from erosion, storm surges, and tsunamis.
- Mangroves are also a source of livelihood for many coastal communities, as they provide resources such as timber, fuelwood, and honey.
Mangrove forests are unique and fascinating ecosystems that play a vital role in maintaining the health of coastal ecosystems. India is home to some of the most beautiful and important mangrove forests in the world, which are critical for protecting the coastlines from erosion, storm surges, and tsunamis. The top 10 mangrove forests in India are a must-visit for every nature lover, as they offer a variety of ecological, economic, and social benefits. By exploring these forests, we can appreciate the beauty and importance of mangroves, and we can also contribute to their conservation and protection.
You may also like
Corporate Plantations
Biodiversity supported by Mangroves
Indian mangrove forests are renowned for their exceptional biodiversity, boasting a rich tapestry of plant and animal species uniquely adapted to thrive in saline coastal environments. These ecosystems are vital for maintaining ecological equilibrium, providing habitat for diverse flora and fauna, including numerous endangered species. The intricate web of life within mangrove forests supports local livelihoods through activities like fishing, honey collection, and traditional medicine, making their conservation imperative for both biodiversity preservation and community well-being.
Mangrove Conservation
The conservation of Indian mangrove forests is paramount to safeguarding these invaluable ecosystems from a multitude of threats. Pressures such as deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution jeopardize the delicate balance of mangrove ecosystems, endangering the myriad of plant and animal species that call them home. Conservation efforts encompass various strategies, including protected area designation, community-based management initiatives, and restoration projects aimed at mitigating these threats and preserving the ecological integrity of mangrove habitats for future generations.
Climate Resilience
Indian mangrove forests play a crucial role in enhancing coastal resilience to climate change impacts. These resilient ecosystems act as natural buffers against coastal erosion, storm surges, and sea-level rise, shielding adjacent communities and infrastructure from the devastating effects of extreme weather events. Furthermore, mangroves sequester significant amounts of carbon dioxide, mitigating the impacts of climate change by helping to regulate the Earth's climate. Protecting and restoring Indian mangrove forests is thus essential for bolstering coastal resilience and mitigating the adverse effects of climate change on vulnerable coastal communities.
Sustainable Livelihoods supported by Mangroves
The sustainable management of Indian mangrove forests is integral to the well-being of coastal communities, offering a plethora of livelihood opportunities deeply intertwined with these ecosystems. Fishing, shellfish harvesting, honey collection, and eco-tourism are just a few examples of the diverse livelihood activities supported by mangrove forests, providing essential income and resources for millions of people along India's coastline. Balancing the conservation of mangrove ecosystems with sustainable resource utilization is paramount to ensure the long-term viability of these livelihoods and the ecological health of mangrove habitats.
Mangrove Restoration
Restoration initiatives are critical for rehabilitating degraded mangrove areas in India, reviving their ecological functions and enhancing their resilience to environmental stressors. Degradation from anthropogenic activities such as deforestation, aquaculture, and urbanization has resulted in significant loss of mangrove habitat and biodiversity across India's coastlines. Restoration efforts involve replanting mangrove species, restoring hydrological connectivity, and implementing sustainable management practices to promote the recovery of degraded mangrove ecosystems. By restoring these vital coastal habitats, restoration initiatives contribute to biodiversity conservation, climate change mitigation, and the sustainable livelihoods of coastal communities.
Threats to mangroves
Indian mangrove forests face a myriad of threats that endanger their ecological integrity and the invaluable services they provide. Deforestation, primarily driven by urbanization, agriculture, and industrial development, poses a significant threat to mangrove habitats, leading to habitat loss and fragmentation. Pollution from industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, and solid waste further degrades mangrove ecosystems, contaminating waterways and threatening aquatic life. Additionally, aquaculture expansion and unsustainable fishing practices exacerbate pressures on mangrove forests, leading to overexploitation of resources and habitat degradation. Addressing these multifaceted threats requires concerted efforts, including effective regulation, community participation, and sustainable management practices to ensure the long-term survival and ecological sustainability of Indian mangrove forests.
FAQ
What are mangrove forests?
Mangrove forests are unique coastal ecosystems found in tropical and subtropical regions, characterized by salt-tolerant trees and shrubs that grow in intertidal areas
Why are mangrove forests important?
Mangrove forests play a crucial role in coastal protection, biodiversity conservation, carbon sequestration, and providing livelihoods for local communities
Where are mangrove forests located in India?
Mangrove forests in India are primarily found along the coastal regions of states like Maharashtra, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, West Bengal, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands
What are the threats to mangrove forests in India?
Mangrove forests in India face threats from coastal development, pollution, climate change, aquaculture, and unsustainable harvesting practices, leading to habitat loss and degradation
How are mangrove forests conserved in India?
Mangrove conservation efforts in India involve measures like declaring mangrove areas as reserved forests, community engagement, eco-tourism initiatives, and natural regeneration processes
What is the current status of mangrove cover in India?
The mangrove cover in India has shown fluctuations over the years, with efforts to increase conservation and protection leading to some improvements in mangrove cover in certain regions
What is the role of mangrove forests in climate change mitigation?
Mangrove forests are essential in sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping mitigate climate change by storing carbon in their biomass and sediments
How do mangrove forests contribute to biodiversity?
Mangrove forests support a diverse range of plant and animal species, acting as nurseries for fish, providing habitats for birds, and offering refuge for various marine organisms
What are the economic benefits of mangrove forests?
Mangrove forests provide economic benefits through fisheries, timber, ecotourism, and shoreline protection services, contributing to the livelihoods of coastal communities
How can individuals contribute to mangrove conservation in India?
Individuals can support mangrove conservation efforts by raising awareness, participating in community initiatives, avoiding activities that harm mangrove ecosystems, and supporting sustainable practices in coastal areas
Most Popular
Connect with us
-
👥 Corporates
If you are looking for:
- 🌲 Tree Plantation Events
- 📊 CSR Projects
📧 corporate@growbilliontrees.com
📞 +91 9699723523
💬 +91 9325931304 WhatsApp (Only)
🕒 Mon - Sat | 10am - 7pm IST
-
🧩 Tree Plantation NGOs
If you are looking for:
- 💰 Financial Assistance
- 🤝 Operational Support
📧 support@growbilliontrees.com
📞 +91 9699723523
💬 +91 9325931304 WhatsApp (Only)
🕒 Mon - Sat | 10am - 7pm IST
-
🌼 Individuals
If you are looking for:
- 👥 Group Tree Plantation Drive
- 🌳 Bulk Tree Plantation
📞 +91 9699723523
💬 +91 9325931304 WhatsApp (Only)
🕒 Mon - Sat | 10am - 7pm IST





















